 A tutorial on setting static and dynamic IP address when routing via ADSL router
A tutorial on setting static and dynamic IP address when routing via ADSL router

30 Sep 2019 - fubar - Sreekar Guddeti

The reason to set up a ADSL router as a switch was to enhance the WiFi signal at my office desk. However sometimes I need to switch back to the iiscwlan WiFi interface when I move my laptop.
Firstly my laptop WiFi adaptor has connected to the wololo WAP of the ADSL modem+router
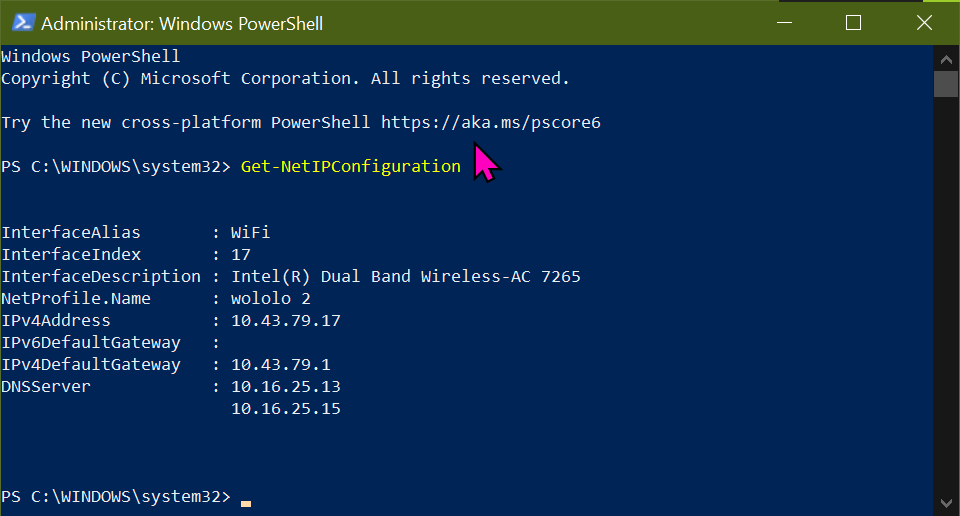
Disconnect from the wololo WAP
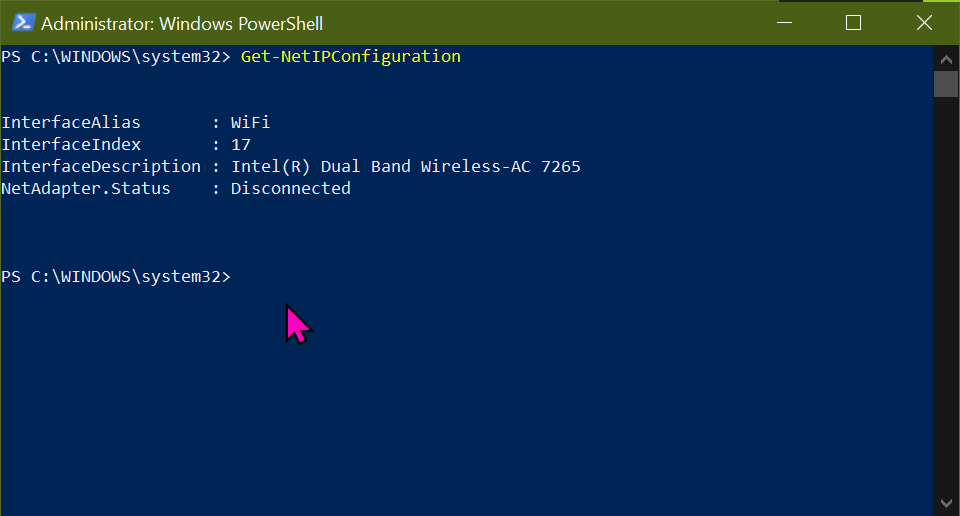
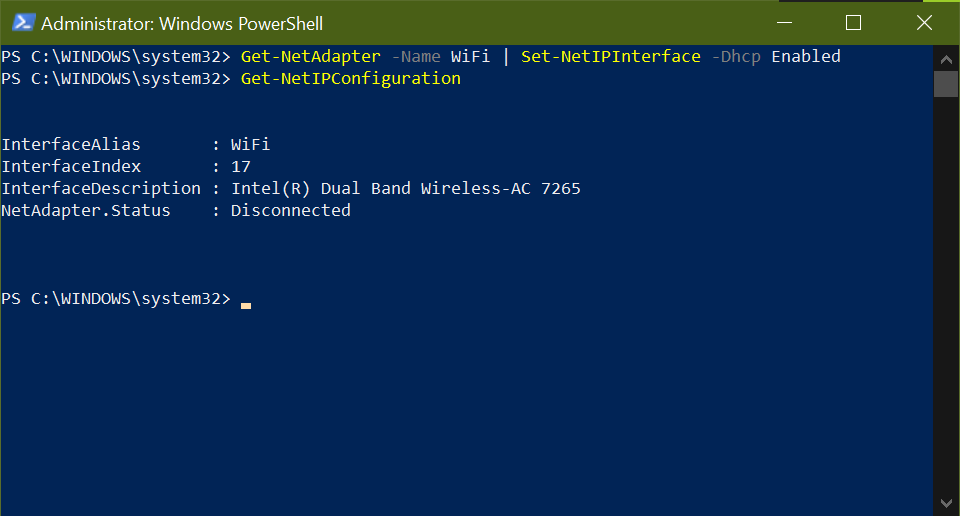
Enable the WiFi interface to have DHCP enabled
Get-NetAdapter -Name WiFi | Set-NetIPInterface -Dhcp Enabled
Connect to the iiscwlan WAP. The DHCP server at 10.43.240.1 and 10.43.79.1 dynamically assigns 10.43.240.122 IP Address to the WiFi interface having index 17 and alias WiFi.
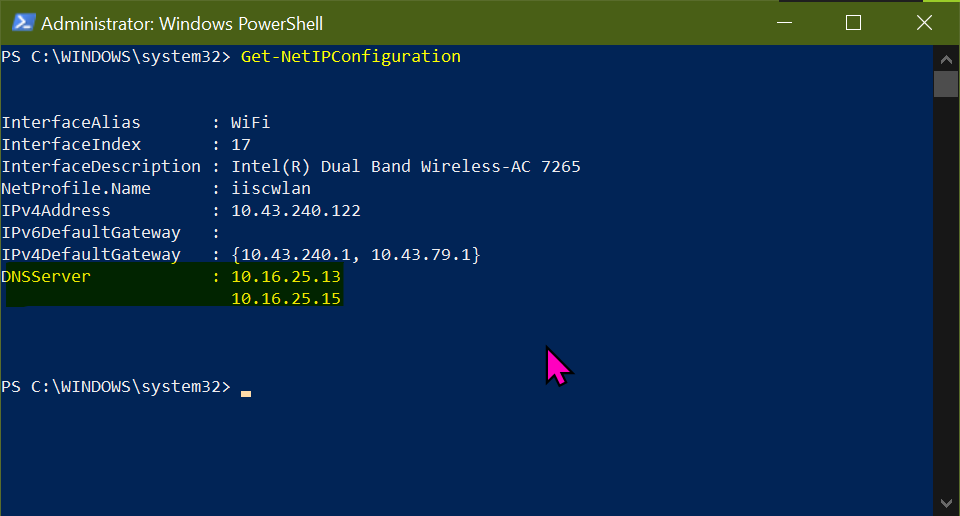
Notice the DNS servers set to 10.16.25.13 and 10.16.25.15. However sometimes these are not set and need to be fetched from the DHCP servers
Set-DnsClientServerAddress -InterfaceIndex 17 -ResetServerAddresses
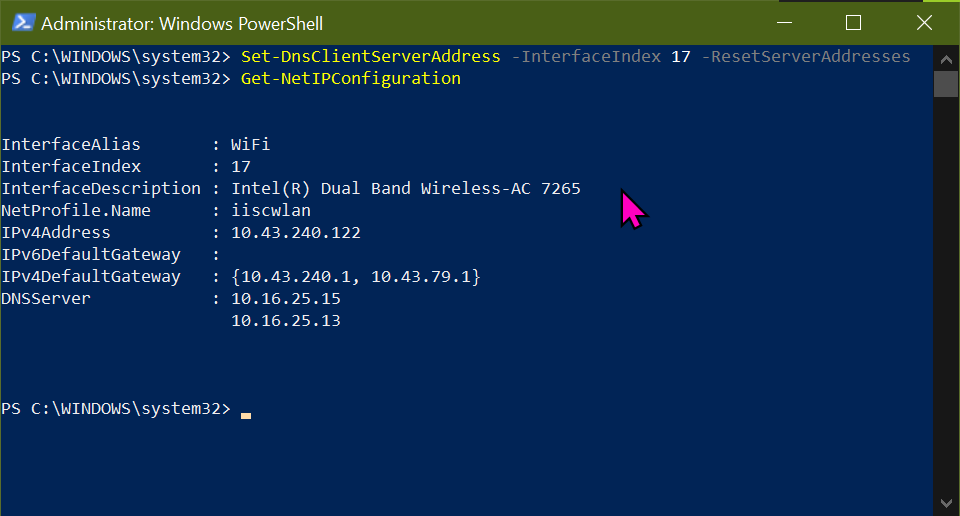
In this way, the IP set dynamically. Thats it!
Run a powershell as an Administrator and check the interface index for the WiFi interface. The Interface has index 17 with alias WiFi. It is connected to the iiscwlan WAP using the IP address 10.43.240.122.
GetNetIPConfiguration
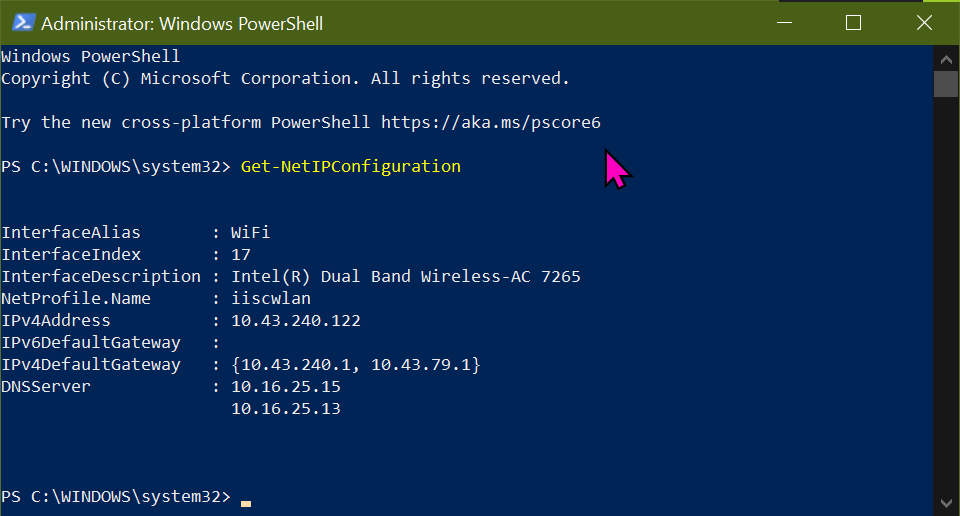
Disconnect from the iiscwlan WAP.
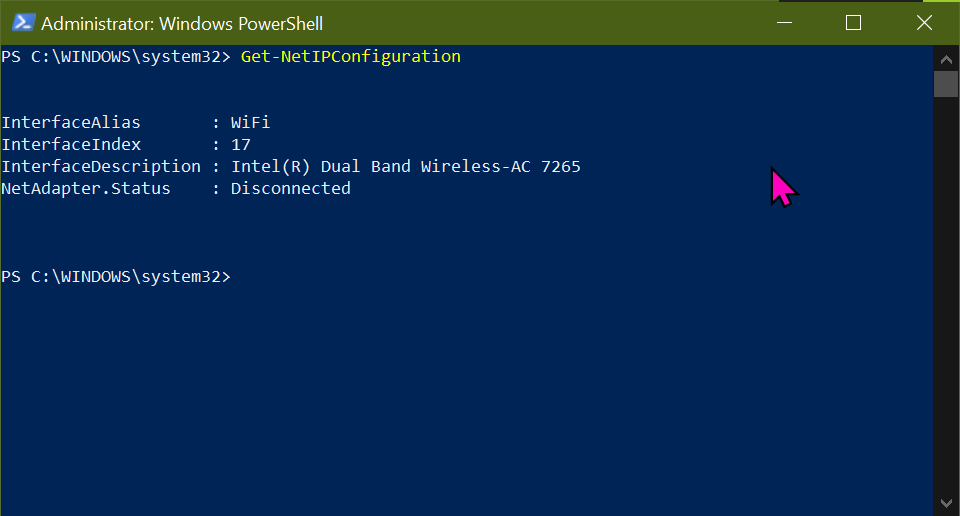
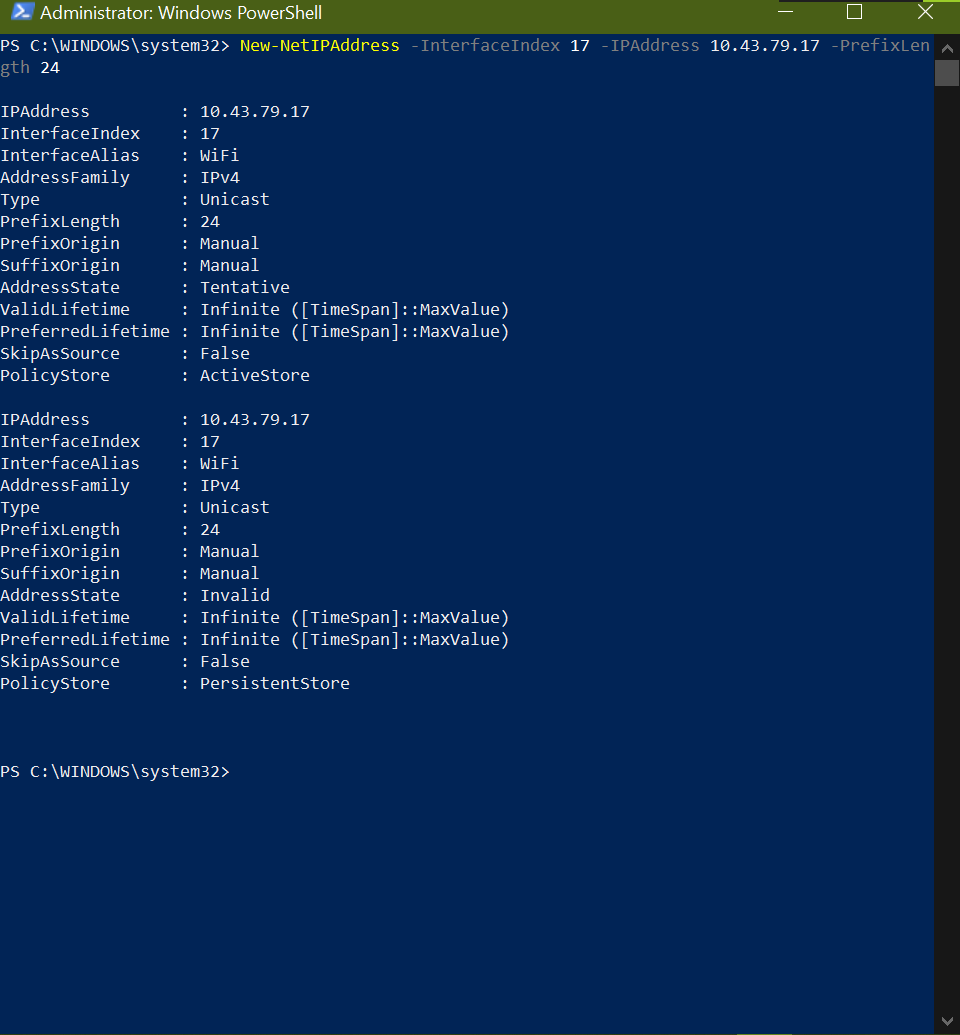
To connect to the wololo WAP we need to know its network address. We know it belongs to 10.43.79.x network address with the available IP addresss starting from 10.43.79.16-255 as the router addresss is 10.43.79.1. Let us set the IP address of the WiFi interface to belong to this range. Let us reserve 10.43.79.16 for the desktop computer’s ethernet interface.
New-NetIPAddress -InterfaceIndex 17 -IPAddress 10.43.79.17 -PrefixLength 24 -DefaultGateway 10.43.79.1
This pops a Windows System Error 87 which says that the default Gateway already exists. Let us remove the Default Gateway option and try again
New-NetIPAddress -InterfaceIndex 17 -IPAddress 10.43.79.17 -PrefixLength 24
Again pops up an Windows System Error 87
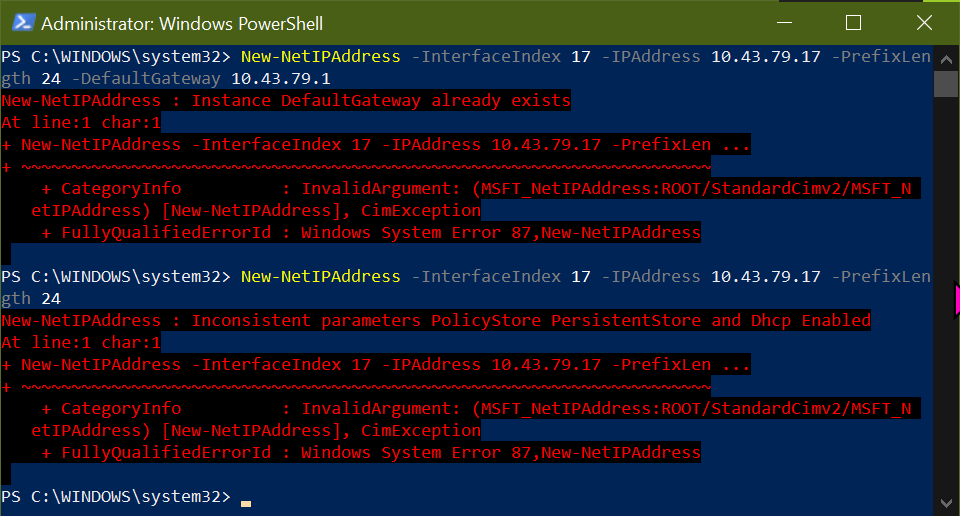
To resolve this first connect to the
wololoWAP then execute the command without the default gateway as already the previousiiscwlanWAP had the same default gateway10.43.79.1
We need to set the DNS servers.
Set-DnsClientServerAddress -InterfaceIndex 17 -ServerAddresses 10.16.25.13, 10.16.25.15
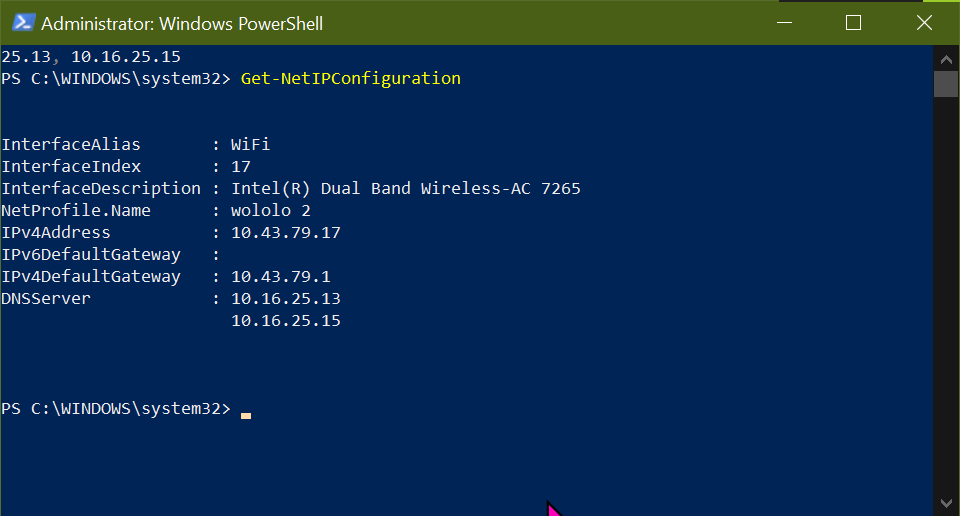
In this way, the IP set statically. Thats it!
Entering these commands is useful. However due to the correct sequence required as well as accuracy requirements, it is better to have a script individually for the static or dynamic setting of IP addresses.
Thanks to Python’s scripting capability to handle system command execution, we use the subprocess module for the task
#!python
'''Script to set Static IP to the WiFi adaptor of laptop.
so that it belongs to the same network address range
as that of the WAP of the router configured to work like a switch.'''
import subprocess
staticIP = '''netsh interface ip set address name="WiFi" static 10.43.79.17 255.255.255.0 10.43.79.1'''
command1 = staticIP.split()
subprocess.run(command1)
staticDNS1 = '''netsh interface ip set dns name="WiFi" static 10.16.25.13'''
command2 = staticDNS1.split()
subprocess.run(command2)
staticDNS2 = '''netsh interface ip add dns name="WiFi" 10.16.25.15 index=2'''
command3 = staticDNS2.split()
subprocess.run(command3)
#!python
'''Script to set Dynamic IP to the WiFi adaptor of laptop
so that it auto configure to have an IP address that
belongs to the same network address as that of the iiscwlan WAP.'''
import subprocess
dhcpCommand = '''netsh interface ip set address "WiFi" dhcp'''
command = dhcpCommand.split()
subprocess.run(command)